
You likely won’t damage your CPU by adjusting other settings due to built-in safety features, but unless you know exactly what these settings do and how they will impact your CPU, sticking with those three fundamentals might be best. The Advanced Tuning section provides many settings you can experiment with, but if you’re new to overclocking, the primary settings to focus on are the Processor Core Ratio, Processor Cache Ratio, and potentially the Core Voltage. This means that if you set the Vcore to 1.1V, and then add an offset of +0.2V, you will be effectively applying a Vcore of 1.3 volts.

If you want to change the CPU Vcore (core voltage) to a specific value, simply select it with the “Core Voltage” slider.When changing these settings, it’s best not to exceed changes of 0.05V at a time. This will add your current Vcore to the value selected. If you don’t know your default Vcore but still want to increase it, you can use the “Core Voltage Offset” slider. These can be increased in order to keep up with higher core ratios if you are encountering system instability. For a CPU to run at faster speeds, it might require more power in order to remain stable, which is where adjusting the Vcore becomes important. i shouldn t install intel xtu in first place.Another section allows you to adjust the Vcore (Core Voltage). i will never be able to have those settings as my defaults? and what kind of damage can those new defaults settings do to my cpu? i m so lost. It does not do anything consistently.ĭifferent Lenovo power profiles might be changing your TDP settings. It will apply the voltage changes consistently. Often times they abandon it because it is unreliable and switch to ThrottleStop after that.

Most users go with Intel XTU first because obviously, it was written by Intel. You can use ThrottleStop to do an undervolt.

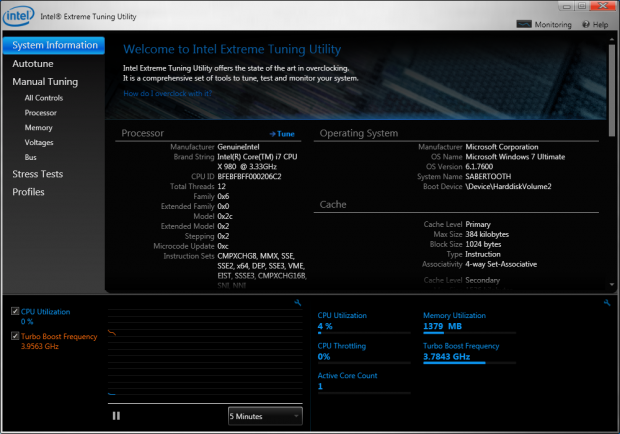
Try adjusting them in this window back to your default values and then reboot and check HWiNFO again. In the TPL window, it will show you what your long and short turbo power limits are set to.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
